今天我們要來實作倒排索引的空間壓縮。這裡我們會利用昨天文中介紹的VByte壓縮法壓縮倒排索引中的文件ID doc_ids 以及文件-詞頻列表 doc_term_freqs 。
在昨天的文中,我們有附上Vbyte壓縮和解壓縮的演算法,我們將開發成以下兩個方法:
def vbyte_encode(num):
# out_bytes 儲存轉換成Vbyte壓縮後的格式
out_bytes = []
while num >= 128:
out_bytes.append(int(num) % 128)
num /= 128
out_bytes.append(int(num) + 128)
return out_bytes
def vbyte_decode(input_bytes, idx):
x = 0 # 儲存解壓縮後的數字
s = 0
consumed = 0 # 記錄花了多少位元組來解壓這個數字
while input_bytes[idx + consumed] < 128:
x ^= (input_bytes[idx + consumed] << s)
s += 7
consumed += 1
x ^= ((input_bytes[idx + consumed]-128) << s)
consumed += 1
return x, consumed
單元測試壓縮和解壓縮過程正確性:
for num in range(0, 123456):
vb = vbyte_encode(num)
dec, decoded_bytes = vbyte_decode(vb, 0)
assert(num == dec)
assert(decoded_bytes == len(vb))
正確地開發了VByte壓縮和解壓縮之後,我們來修正原本的 InvertedIndex 類別以支援VByte壓縮。需要注意的是, doc_ids 的部份是要壓縮文件ID之間的間隔而不是文件ID本身。我還寫了一個輔助方法 decompress_list 來幫助我們更簡單地將列表解壓縮。
def decompress_list(input_bytes, gapped_encoded):
res = []
prev = 0
idx = 0
while idx < len(input_bytes):
dec_num, consumed_bytes = vbyte_decode(input_bytes, idx)
idx += consumed_bytes
num = dec_num + prev
res.append(num)
if gapped_encoded:
prev = num
return res
class CompressedInvertedIndex:
def __init__(self, vocab, doc_term_freqs):
self.vocab = vocab
self.doc_len = [0] * len(doc_term_freqs)
self.doc_term_freqs = [[] for i in range(len(vocab))]
self.doc_ids = [[] for i in range(len(vocab))]
self.doc_freqs = [0] * len(vocab)
self.total_num_docs = 0
self.max_doc_len = 0
for docid, term_freqs in enumerate(doc_term_freqs):
doc_len = sum(term_freqs.values())
self.max_doc_len = max(doc_len, self.max_doc_len)
self.doc_len[docid] = doc_len
self.total_num_docs += 1
for term, freq in term_freqs.items():
term_id = vocab[term]
self.doc_ids[term_id].append(docid)
self.doc_term_freqs[term_id].append(freq)
self.doc_freqs[term_id] += 1
# 壓縮文件ID之間的間隔
for i in range(len(self.doc_ids)):
last_docid = self.doc_ids[i][0]
for j in range(len(self.doc_ids[i])):
if j != 0:
ori_docid = self.doc_ids[i][j]
self.doc_ids[i][j] = vbyte_encode(self.doc_ids[i][j] - last_docid)
last_docid = ori_docid
else:
self.doc_ids[i][0] = vbyte_encode(last_docid)
self.doc_ids[i] = sum(self.doc_ids[i], [])
# 根據詞頻壓縮
for i in range(len(self.doc_term_freqs)):
for j in range(len(self.doc_term_freqs[i])):
self.doc_term_freqs[i][j] = vbyte_encode(self.doc_term_freqs[i][j])
self.doc_term_freqs[i] = sum(self.doc_term_freqs[i], [])
def num_terms(self):
return len(self.doc_ids)
def num_docs(self):
return self.total_num_docs
def docids(self, term):
term_id = self.vocab[term]
# 解壓縮
return decompress_list(self.doc_ids[term_id], True)
def freqs(self, term):
term_id = self.vocab[term]
# 解壓縮
return decompress_list(self.doc_term_freqs[term_id], False)
def f_t(self, term):
term_id = self.vocab[term]
return self.doc_freqs[term_id]
def space_in_bytes(self):
# 這裡現在假設數字都是位元組型態
space_usage = 0
for doc_list in self.doc_ids:
space_usage += len(doc_list)
for freq_list in self.doc_term_freqs:
space_usage += len(freq_list)
return space_usage
compressed_index = CompressedInvertedIndex(vocab, doc_term_freqs)
print("documents = {}".format(compressed_index.num_docs()))
print("unique terms = {}".format(compressed_index.num_terms()))
print("longest document = {}".format(compressed_index.max_doc_len))
print("compressed space usage MiB = {:.3f}".format(compressed_index.space_in_bytes() / (1024.0 * 1024.0)))
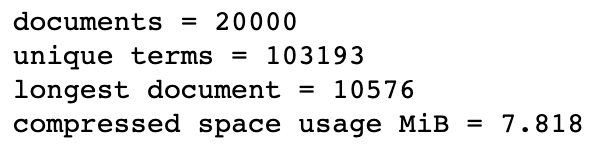
在資料不變的情況下,我們的空間使用已經從58.187MiB降到了7.818MiB。
最後,我們來測試原本的倒排索引及VByte壓縮後的倒排索引結果有沒有改變(理論上結果該相同)。
# 確認是否和先前結果相同
query = "south korea production"
stemmed_query = nltk.stem.PorterStemmer().stem(query).split()
comp_results = query_tfidf(stemmed_query, compressed_index)
for rank, res in enumerate(comp_results):
print("排名 {:2d} DOCID {:8d} SCORE {:.3f} 內容 {:}".format(rank+1,res[0],res[1],raw_docs[res[0]][:75]))

不論DocID排名或是TF-IDF分數都沒有改變,壓縮結果正確。
今天的Jupyter Notebook在這裡。
